
What is Kafka ? Apache Kafka Explained
Kafka is the open source messaging system that was built by LinkedIn and later donated to the Apache software foundation. The purpose of writing kafka is to manage large amounts of data in real time. Kafka is suitable for creating systems that can react to events as they occur. It combines messaging, storage, and stream processing, allowing the storage and analysis of both historical and real-time data.
Kafka structures data into categories called “Topics”. There are two sides and in between there is a kafka server that includes topics. Producers (send data) put messages into the topics and other side is consumer (read data) receive them. Kafka ensures that the system is reliable and will continue to work even if some parts fail. RealCloud offers reliable and high-performance Apache Kafka services to enable seamless real-time data streaming and event-driven architectures.
Kafka Provides Three Main Functions :
- Publish and subscribe to record streams.
- Efficiently store record streams in the order the records were created.
- Process record streams in real-time
Core Component of Kafka
Kafka Broker :
Kafka broker is a server that runs Kafka and stores data. Kafka cluster consists of multiple brokers that work together to provide scalability, fault tolerance, and high availability. Each broker is responsible for storing and presenting data related to the topic.
Producer :
Producer is a service or application that sends messages to the kafka topic. By this process, push data into the kafka system. Producers decide which topic a message should be sent to, and Kafka handles it efficiently based on the partitioning strategy.
Consumer :
Consumer is an application that reads messages from Kafka topics. Kafka allows consumer groups, where multiple consumers can read the same topic, but Kafka ensures that each message is processed by only one consumer in the group.
It helps in load balancing and allows consumers to read messages. Partitioning allows you to parallelize a topic by dividing the data of a particular topic across multiple brokers.
ZooKeeper :
ZooKeeper ensures high availability by ensuring that the Kafka cluster remains operational even if a broker fails. Kafka uses Apache ZooKeeper to manage metadata, control access to Kafka resources, and handle leader election and broker coordination. The combination of Kafka Zookeeper helps a lot.
Important Concept of Apache Kafka
Topic Partitioning: Kafka topics are divided into multiple partitions, which allows you to split data across multiple brokers.
Consumer Group: A consumer group in Kafka consists of a set of consumer processes that subscribe to a specific topic.
Node: A node is a single computer in an Apache Kafka cluster.
Replicas: A replica of a partition is a “backup” of the partition. Replicas can never read or write data. These are used to prevent data loss.
Producer: The application that sends the message.
Consumer: The application that receives the message.
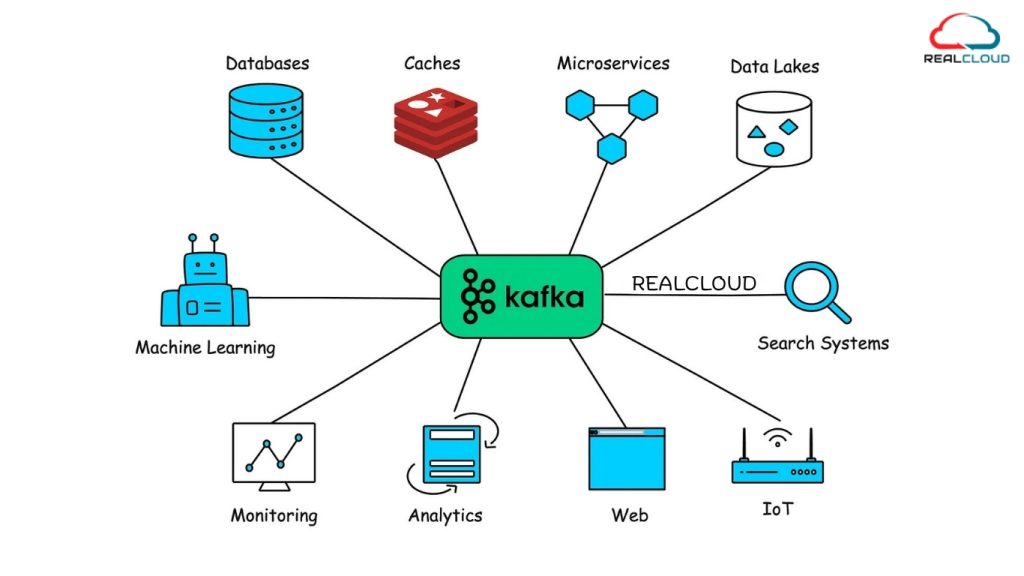
Why is Apache Kafka Needed?
With businesses collecting massive amounts of data in real time, Kafka solves several key problems.
Real-time processing: Kafka is optimized to handle real-time data processing, allowing businesses to process and act on data.
Fault-tolerant: Kafka ensures that data is not lost even if some parts of the system go down, making it a highly reliable messaging system.
Scalable: Kafka scales horizontally by adding more brokers, enabling it to handle increasing data loads and a growing number of producers and consumers.
Event-Driven Architecture: Kafka empowers event-driven architecture, allowing systems to react to events in real-time without constantly polling for changes.
How does Apache Kafka Work?
By following the simple steps, Apache Kafka moves data from one place to another in a smoother way.
Step 1 – Producers Send Data
Step 2 – Kafka Stores Data
Step 3 – Consumers Read Data
Step 4 – Kafka Balances the Load
Step 5 – Data is Processed and Used
Common Use Case of Apache Kafka
Apache Kafka is used widely across various industries. Here, we are mentioning some popular use cases.
Real-time analysis: Real time data processing for live analysis, such as monitoring user activities or stock prices.
Event-Driven Applications: Kafka empowers event-driven architectures, ensuring that systems respond in real-time to events such as user actions, transactions, or sensor data.
Log aggregation: Collecting logs from multiple systems into a centralized logging system for better analysis and monitoring.
Stream Processing: Kafka, with tools like Apache Flink or Apache Spark, is used to process streams of data in real time.
Data Integration: Kafka integrates data between different systems, such as moving data between different microservices or syncing databases.
Benefits of Apache Kafka
1- Handles Large Data Easily
2- Reliable & Fault Tolerant
3- Real Time Data Processing
4- Easy System Data Integration
5- Works with any Data Types
6- Strong Community Support
Limitation of Apache Kafka
1- Difficult to Set Up
2- Storage can be expensive
3- Message Order Issues
4- No Built-in Processing
5- Needs High Resources
6- Not Ideal for Small Messages
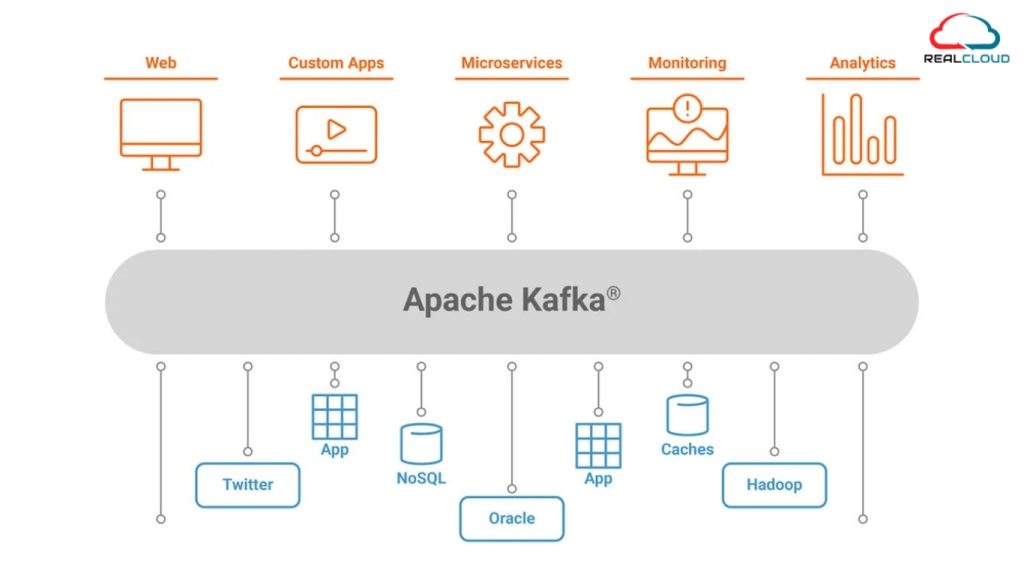
Features of Apache Kafka
Scability :- Kafka can handle huge amounts of data by breaking it into smaller partitions and distributing them across multiple servers. This means it can scale as a business’s data needs grow.
Fault Tolerance :- Even if some servers fail, Kafka continues to run smoothly because it creates copies (replications) of the data. This ensures that no important information is lost.
Flexibility :- Kafka can work with any type of data because it stores information as byte arrays. Whether it’s logs, events, or structured records, Kafka can handle everything.
Offset Management :- Consumers (applications reading the data) don’t have to start from scratch every time they can pick up right where they left off. This makes it easier to process data without any interruption.
Apache Technologies Frequently Used With Kafka
Apache technologies that help improve data management, processing, and integration.
1- Apache Zookeeper :- Kafka relies on Apache ZooKeeper architecture to manage cluster information, such as tracking active brokers and handling leader elections. This ensures that the system runs smoothly.
2- Apache Avro :- Kafka often uses Avro for data serialization. This makes the storage and sharing of structured data more efficient as well as allows for schema changes without affecting compatibility.
3- Apache Flink :- Kafka and Flink work together to process real-time data streams. Flink helps analyze data as it arrives, making it useful for live monitoring, fraud detection, and event-driven applications.
4- Apache Spark :- Spark can read data from Kafka for both real-time and batch processing. It is widely used for machine learning, ETL (extract, transform, load) tasks, and big data analytics.
5- Apache Hadoop :- Kafka streams large amounts of data, and Hadoop provides long-term storage for in-depth analysis. This combination is useful for businesses handling large datasets.
6- Apache Storm :- For real-time, low-latency processing, Storm works well with Kafka. This helps with applications like tracking live events, detecting unusual activities, or updating dashboards in real-time.
7- Apache Camel :- Kafka is often integrated with various systems using Camel, which acts as a bridge between Kafka and various APIs, databases, or cloud services. This simplifies message routing and data conversion.
8- Apache NiFi :- It automates the flow of data between Kafka and other sources or destinations. It helps in building scalable data pipelines without any extensive coding.
Conclusion
Apache Kafka is a powerful publish subscribe messaging system designed for high-throughput, real-time data streaming and processing. Apache Kafka is a powerful tool for handling real-time data streams, providing unmatched scalability, reliability, and performance. Whether you’re building an event-driven architecture, implementing real-time analytics, or collecting logs, Kafka provides a flexible, fault-tolerant, and efficient solution. With its wide range of use cases and seamless integration with other tools like Apache Flink, Spark, and Hadoop, Kafka remains the preferred choice for organizations looking to process large amounts of data in real-time.